Round Head Mat,AB Mat,Mat Jiangsu Laiao Material Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.laiaomaterial.com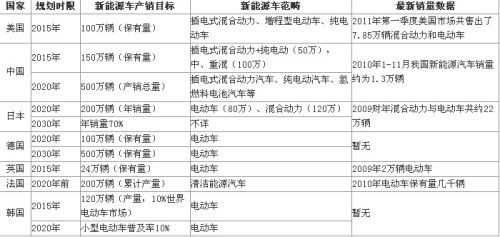 On the one hand, the government is actively planning and on the other, the market is unresponsive. This is the current status of the development of new energy vehicles in the world.
On the one hand, the government is actively planning and on the other, the market is unresponsive. This is the current status of the development of new energy vehicles in the world.
In countries that propose relatively clear plans for new energy vehicles, except China, other developed countries have a very strong automotive industry base. For example, the United States, Germany, Japan, South Korea, France, and the United Kingdom. These countries are also the world’s major automobile production and sales countries.
Judging from the timetable for the planning of new energy vehicles in various countries, government agencies or associations in charge of the automobile industry in the United States, China, South Korea, and the United Kingdom have proposed more recent production and sales targets - a certain amount or amount of production and sales within 5 years. This to a certain extent reflects the more urgent mentality of these countries in developing new energy vehicles.
In the new energy vehicle plans put forward by countries such as Germany, Japan, and France, the deadlines for realizing the quantitative production and sales scale targets are set relatively late. They set the production and sales targets for 2020 respectively, of which Germany and Japan are also right. In 2030, a relatively clear production and sales target was also proposed. The long-term strategy for the development of new energy vehicles in these countries is determined.
The production and sales planning of new energy vehicles in the world's major automotive markets is based on the 2015 target for production and sales in various countries. The United States has the greatest ambitions. The United States plans to maintain the number of electric vehicles in the country by 1 million in 2015. Although China proposed to sell 1.5 million new energy vehicles by 2015, according to its definition of new energy vehicles, its sales of plug-in hybrid and pure electric vehicles are only 500,000, and all others are hybrid Power models. The UK’s goal is the most “conservative†compared to other countries. In 2015, the production and sales target of electric vehicles is only 240,000 vehicles.
In the 2020 target, China appears to be “aggressive,†and the Chinese government has proposed a grand target of 5 million new energy vehicles in 2020. This target does not include ordinary hybrid vehicles. . In addition, Japan proposes to achieve annual sales of 2 million new energy vehicles in 2020, which will account for approximately 50% of its new vehicle sales, of which the sales target for electric vehicles is 800,000. This goal is also extremely ambitious; the French government plans to By the year 2020, the goal of achieving a cumulative output of 2 million clean energy vehicles will be lower than in other countries. However, the French government’s determination is also very large compared to its current possession of less than 10,000 vehicles.
Judging from the definition of new energy vehicles, most countries will lock the development direction of future new energy vehicles into electric vehicles, while using hybrid power as a transitional product. For example, in the production and sales planning of new energy vehicles set by countries such as Germany, the United Kingdom, and South Korea, only electric vehicles are included. In the definition of new energy vehicles, the United States also emphasized that only plug-in hybrid power is included in the statistics of new energy vehicles. China's mid-range and heavy-duty vehicles included in its 2020 new energy vehicle production and marketing plan and 2015 plan are also missing.
Finally, based on the sales status of the above-mentioned national new energy vehicles, the sales volume of the United States and Japan is relatively high, and it is also more feasible to set goals. In the first quarter of 2011, the sales volume of new energy vehicles in the US market reached 78,500 units, and the annualized conversion rate reached 300,000 units. In Japan, the sales of new energy vehicles in 2009 fiscal year (as of March 2010) were approximately 220,000 units, accounting for approximately 10% of its new car sales. Sales in China, France, and the UK are far from the goals they set. For example, in the first 11 months of 2010, sales of new energy vehicles in China were only 13,000, while the 2015 target was as high as 1.5 million. There is no reliable data for analysis in Germany and South Korea. In general, the status quo of electric vehicles is not optimistic as compared to the national targets. There are still many uncertainties in the road of electric vehicles.