Generally have two kinds of structure: first half open, is composed of a rear cover plate and blades, the structure, the efficiency of the Impeller lower, in order to improve the efficiency to be matched with a seal ring which can adjust clearance; another half open, is composed of a front cover plate and blades. The application and closed the same impeller sealing ring, efficiency and closed impeller is basically the same as the blades, and in addition to transport liquid, also has back blade or vice impeller seal. The semi open impeller is suitable for conveying liquid containing solid particles, fibers, etc.. Semi open impeller manufacturing is difficult, low cost, and adaptability, in the oil refining and chemical industry with a gradual increase in the application of centrifugal pump, and for the transport of water and water approximation of the liquid.
Photo of our Impeller:
Open impeller
Only blades and blades to strengthen the reinforcement, no front and back cover of the impeller (open impeller blade number less 2-5). Impeller efficiency is low, the application is less, mainly used for conveying high viscosity liquid, as well as slurry liquid.
Blade of centrifugal pump impeller is generally backward curved blade. There are two kinds of cylindrical and twisted, the application of twisted blades can reduce the load of the blade, and can improve the suction performance of centrifugal pump, improve the anti cavitation ability, but the manufacture is difficult, the cost is higher.
Centrifugal pump for oil refining and chemical industry requires impeller for casting or whole welding seam welding of the integral impeller. Special centrifugal pumps for chemical use in the manufacture of metal materials (such as iron and its alloys), which are used in the manufacture of poor performance, such as iron and its alloys. The geometric accuracy and surface finish of the welded impeller are superior to the casting impeller, which is beneficial to the improvement of the efficiency of the centrifugal pump.
Shape classification
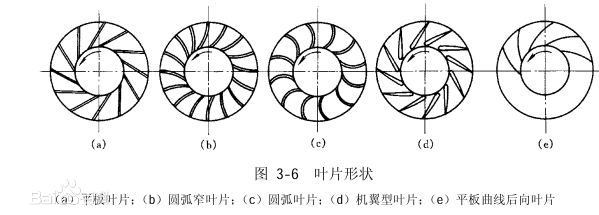
The shape of the blade centrifugal fan impeller has several single plate, arc type and wing type etc.. Airfoil blade has good aerodynamic characteristics, high efficiency, good strength and stiffness. The disadvantage is that the manufacturing process is complex, and when the transmission of high dust concentration of the gas, the blade is easy to wear, blade wear, the impurities into the blade, so that the impeller lost balance and vibration. The flat straight blade is simple, but the flow characteristics are poor, and the efficiency is quite close to the efficiency of the other working conditions when the flat curve is compared with the airfoil blade, and the efficiency is lower than the highest efficiency point.
Forward impeller
The front impeller generally adopts circular arc blade, and the rear direction impeller, the large fan adopts the airfoil blade, and the wind turbine of the coal fired boiler with low dust removal efficiency can adopt the circular arc type or the flat plate type blade. The centrifugal fan with flat blade is more.
(a) flat blade; (b) arc narrow blade; (c) arc blade; (d) wing blade; (E) flat curve back to blade
Compression impeller
Working round. The only component of the air flow in a centrifugal compressor. The most important parts on the rotor. Generally by the wheel, wheel cover and blade and other parts of the composition. Under the action of the impeller blades, the rotating speed of the leaf rotation, the gas is affected by the centrifugal force of the rotation, as well as in the impeller of the diffuser flow, so that it can be improved through the pressure of the impeller.
Requirements for impeller
(1) can be given a larger energy; (2) gas flows through the impeller loss should be small, namely the gas flows through the impeller efficiency to be high; (3) gas outflow impeller parameters when appropriate, the gas flowing behind the fixing element flow loss is smaller; (4) type of impeller can make or overall performance curves of the stable operating region and the efficiency range is wide. Normally divided into closed, semi open and open type impeller.
The impeller is composed of a wheel hub and a blade in a wind turbine. The wind passes through the impeller, drives the impeller to rotate, which drives the generator to rotate, and the wind energy is converted into electric energy. At this time, the rotating impeller with large enough on the windward side, to extract enough energy from the wind; at the same time, when the wind speed is too large, can automatically adjust the blade windward angle to avoid due to the stress and mechanical damage.
Impeller material
Cast iron, bronze, stainless steel, manganese bronze, Monel alloy, INCONEL, and non metal materials.
Non metallic materials
PPS plastic, phenolic resin, etc..
Impeller Boat Impeller,Centrifugal Impeller,Marine Impeller,Water Pump Impeller Unisite Group Ltd. , https://www.unisitemarine.com
3D printing technology is difficult to use in the shipbuilding industry for a short time, but it will have a revolutionary impact on the traditional shipbuilding industry.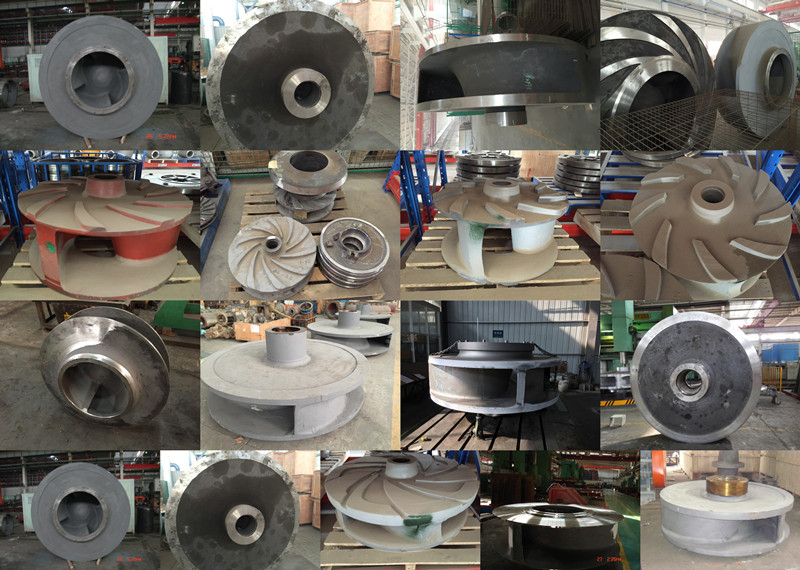 
As an important symbol of the third industrial revolution, 3D printing technology is considered to be an important opportunity to promote a new round of industrial revolution. With the concept of "smart manufacturing" and "Industry 4.0", the application of 3D printing technology in the field of shipbuilding has become a hot topic.
This paper uses the literature research method and observation method to take the impact of 3D printing technology on the manufacturing industry as the starting point, comprehensively analyzes the current situation of 3D printing technology and industrial development, and believes that 3D printing technology is difficult to be widely used in the shipbuilding industry for a short time, but It will have a revolutionary impact on the traditional shipbuilding industry for a long time.
Mainstream 3D printing technology
3D printing technology is a kind of rapid prototyping technology, also known as additive manufacturing. The basic principle is to make a 3D model by computer aided design or scanning; cut into an infinite number of sections according to a certain coordinate axis, then print them one by one, and stack them together according to the original position to form a solid three-dimensional model. . The process flow is generally divided into three steps, namely three-dimensional modeling, product molding and post-processing of finished products.
There are currently a dozen practical rapid prototyping technologies, but almost all technologies are based on the following three basic principles.
One is to form a casting or semi-liquid material by squeezing the print head. The most common method is to squeeze the continuous flow of thermoplastic, which quickly solidifies as it leaves the printer nozzle. The “melt deposition moldingâ€, “plastic printingâ€, “fuse modelingâ€, “fuse manufacturing†or “melt deposition method†currently on the market are products of this principle, just because of intellectual property issues. The name is different.
Second, a physical layer is formed by turning an uncommon liquid called "photosensitive resin" into a solid. Such liquids become hard when exposed to lasers or other light sources, such as "photocuring rapid prototyping processes", "photosensitive resin jetting", "multi-nozzle modeling" and "inkjet photosensitive resins".
Third, the model is made by bonding an unusual fine powder layer by layer. This "adhesion of particulate material" can be achieved either by spraying liquid glue or by bonding each powder layer, or by melting the powder particles by laser or other heat source. Such as "adhesive spray technology", "selective laser sintering technology", "directional energy deposition technology" and "electron beam melting technology".
There is also a "layered solid manufacturing technology" that uses paper cutters to bond paper, plastic or metal foil together, and then uses a supply device to push the material onto the production platform, using rollers (usually heated). The thin plate is rolled, and the laser at the top is cut on the sheet to cut the outline of the object layer, and then the production platform is lowered. This process is repeated until the entire object is printed. However, companies that offer this technology have closed down, and several other manufacturers of printers that produce this technology have also left the 3D printing market, so the technology is considered dead.
The status quo of 3D printing technology
The application of 3D printing technology can be divided into industrial and consumer. In 1986, 3D Systems was established in the United States. Two years later, the first industrialized "3D printing" device, the SLA-250, was launched, which formed a huge market in just a few years. 3D printing equipment users have rapidly expanded to small and medium-sized enterprises and even 3D printing personal enthusiasts by large enterprises and scientific research institutions that originally developed their own products. Currently, there are two 3D printer manufacturing giants around the world - 3D Systems and Stratasys, both listed in the US. As a leader in industrial-grade 3D printing, the two companies are expanding their downstream areas, enhancing software and solution investment, and industry integration, ranging from biological blood vessels to aircraft titanium alloy main bearing components. With the development of 3D printing technology, more and more manufacturers all over the world have entered the field of 3D printing, such as Voxeljet in Germany and ExOne in the US, such as small and medium-sized 3D printing manufacturers. The application of 3D printing technology has also expanded from initial research to medical, clothing, construction, dot-adding, mechanical manufacturing and industrial modeling.
With the maturity of global 3D printing technology, the 3D printing market has entered a high growth. Canalys expects market sales of 3D printers to reach $16.2 billion (including printers, materials and related services) by 2018, showing an average annual growth rate of 40% to 50%. Juniper Research expects the market size of China's 3D printers and related materials to increase from the current $75 million to $1.2 billion in 2018, showing explosive growth and increasing its share of the global market to 7.4% by 2018 (see Table 1). .
3D printing technology and traditional technology
Compared with traditional material removal, that is, cutting technology, 3D printing technology has the advantage of eliminating the need for traditional tools and fixtures and multiple processing steps to quickly and accurately create complex shapes, thus significantly reducing the processing time. Therefore, the more complex the structure of the manufactured product, the more obvious its advantages.
While 3D printing technology has many advantages, it also has many limitations (see Table 2).
Application of 3D printing technology in shipbuilding
At present, 3D printing technology has not been widely used in the shipbuilding industry. This is because the advantages of 3D printing technology cannot be fully determined in the shipbuilding industry.
Limited size
Since 3D printers are an inclusive printing device, products are usually smaller than printers. The structural size of the shipbuilding industry is much larger than the current 3D printing size, making it difficult for 3D printing to print out the structures needed for proper shipbuilding.
Expensive material
At present, suitable materials for 3D printing are plastic, ceramics and alloys, but they are still much more expensive than steel, which is widely used in traditional shipbuilding. Even the use of relatively inexpensive thermoplastics in existing 3D printing is still much more expensive than steel in conventional shipbuilding, and there are not many components for shipbuilding that are suitable for thermoplastics.
Timeliness cannot be played
Although 3D printing eliminates the need for machining or any mold, it can directly produce parts of any shape from computer graphics data, greatly reducing the product development cycle. The traditional shipbuilding industry and supporting industries have improved production efficiency through standardized and large-scale production lines. At present, 3D printing technology is more used to print small-sized, relatively simple parts, and cannot be used to print complex systems.
Low precision and unstable quality
Since 3D printing is a new technology, the current accuracy range is 0.01 mm, which is much lower than that achieved by traditional shipbuilding using "material reduction". In addition, the strength and hardness of mechanical products are much higher than those of 3D printed products.
Conclusion
Whether the cutting-edge and leading 3D printing technology can be widely used in the traditional manufacturing field depends on two aspects of progress: First, the development of 3D printing technology, the emergence of mature and stable 3D printing technology can directly print large-sized, complex components. Second, the traditional ship is a steel sea ship. With the development of material technology, if there is an economical and reliable polymer synthetic material that can replace steel materials, then the use of 3D printing polymer synthetic materials for sea-going ships will become a reality. .
At present, the development of the shipbuilding industry mainly relies on the input of factors, such as the investment of large docks and large factories to increase production capacity. At present, the country is promoting the upgrading of traditional manufacturing, and the shipbuilding industry is also actively promoting digital shipbuilding, such as computer management and 3D modeling. With the development of digitalization, the improvement of intelligence, the development of 3D printing technology and the revolutionary development of materials technology, 3D printing technology will eventually have a revolutionary impact on the traditional shipbuilding industry.